Maintaining your vehicle's essential components is critical for longevity and performance. One often overlooked yet vital element is the timing belt, which plays a crucial role in your engine's operation. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to understand about timing belt maintenance to help prevent costly repairs and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly for years to come.
Understanding timing belts and their function
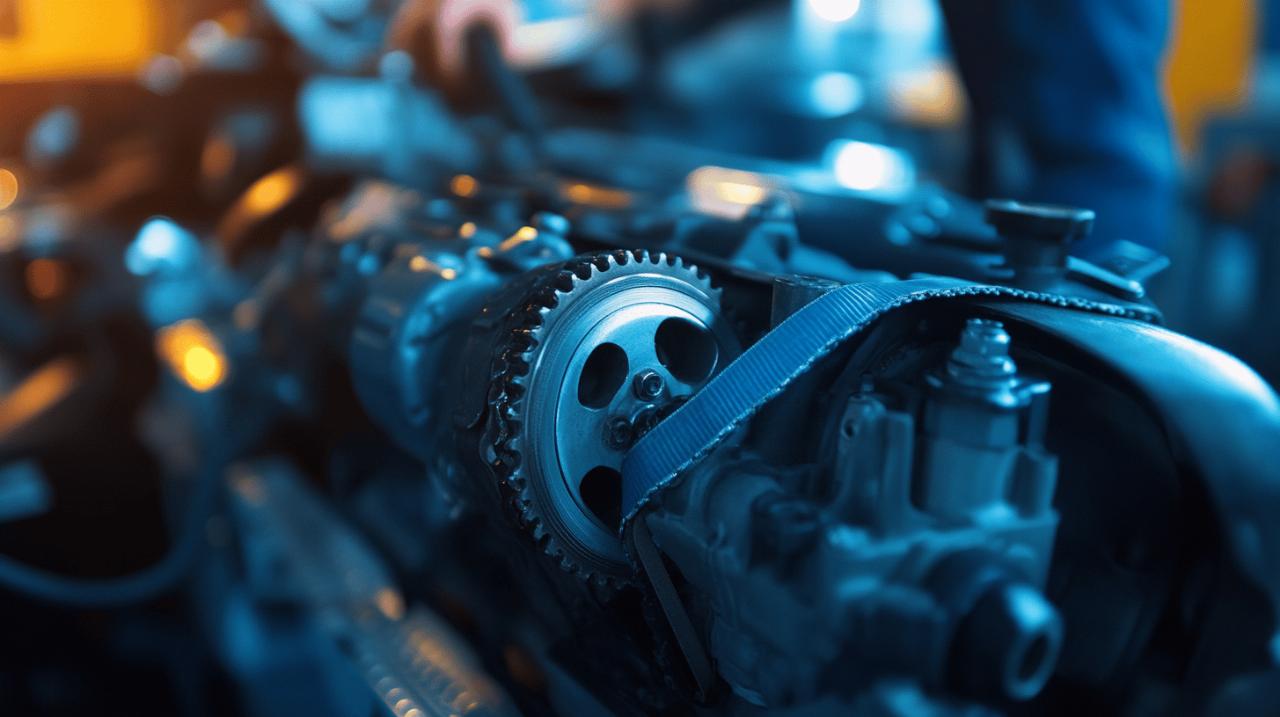
What Is a Timing Belt and What Does It Do?
A timing belt, also known as a cambelt, is a robust rubber belt reinforced with fibres that serves a fundamental purpose in your engine's operation. Motor Publish explains that this component is responsible for synchronising the movement between the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring that the engine valves open and close at precisely the right moments during the combustion process. Without this synchronisation, your engine would not function properly or could sustain serious damage.
Timing belts differ from timing chains in both material and durability. While timing belts are made of rubber and are relatively lightweight, timing chains are constructed from metal and typically offer greater longevity. Some modern vehicles also utilise wet belts, which are rubber-based components that operate in oil and generally require monitoring from around 80,000 miles onwards. You can usually identify whether your vehicle has a timing belt by checking for a plastic cover on the engine; the presence of such a cover typically indicates a timing belt rather than a chain.
Signs your timing belt might need attention
Being aware of potential warning signs can help you avoid catastrophic engine failure. If your engine experiences misfiring, produces unusual ticking sounds, struggles to start, or idles roughly, these could all indicate timing belt issues. Additionally, loss of power, oil leaks, and strange noises from the engine compartment should prompt immediate inspection.
Should a timing belt break while driving, the consequences can be severe. The engine will stop running, potentially leaving you without power steering and making braking more difficult. In interference engines, where the pistons and valves share the same space at different times, a broken timing belt can lead to valves striking pistons, causing extensive and expensive engine damage.
Proper maintenance schedule for timing belts
Manufacturer recommendations for replacement intervals
 Following the manufacturer's recommended replacement schedule is essential for preventing timing belt failure. Generally, timing belts should be replaced every 50,000 to 100,000 miles or every 5 to 10 years, depending on your specific vehicle model. Your vehicle handbook contains detailed information about the recommended interval for your particular make and model.
Following the manufacturer's recommended replacement schedule is essential for preventing timing belt failure. Generally, timing belts should be replaced every 50,000 to 100,000 miles or every 5 to 10 years, depending on your specific vehicle model. Your vehicle handbook contains detailed information about the recommended interval for your particular make and model.
When replacing a timing belt, mechanics often recommend changing related components simultaneously. If your timing belt drives the water pump, replacing both components together is advisable, along with associated parts like tensioners and pulleys. Using an all-inclusive kit ensures all components match and work together optimally. After replacement, the cooling system should be flushed and refilled with the correct coolant to protect the new components.
Factors that impact timing belt lifespan
Several factors can influence how long your timing belt will last. Wear and tear from normal operation is inevitable, but certain conditions can accelerate deterioration. Age-related wear affects timing belts even in vehicles with lower mileage, making regular inspections important regardless of how much you drive.
Environmental conditions also play a significant role in timing belt longevity. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can cause the rubber to become brittle or degrade more quickly. Oil or coolant leaks can contaminate the belt and reduce its lifespan. Regular servicing provides opportunities for mechanics to check for these issues before they lead to belt failure.
The cost of timing belt replacement varies significantly depending on the vehicle make and model. As of April 2025, the average cost is approximately £468, including parts and labour. However, for some luxury vehicles, the bill can exceed £1,000. This investment, while substantial, is minor compared to the potential cost of repairing engine damage caused by a failed timing belt.
